The block header contains the block version number, a timestamp, the hash used in the previous block, the hash of the Merkle Root, the nonce, and the target hash. The block is generated by taking the hash of the block contents, adding a random string of numbers , and hashing the block again.
This arbitrary function is resource-intensive, making it difficult for a bad actor to overtake the network. Processing the hash functions needed to encrypt new blocks requires substantial computer processing power, which can be costly. To entice individuals and companies, referred to as miners, to invest in the required technology, cryptocurrency networks reward them with both new cryptocurrency tokens and a transaction fee.
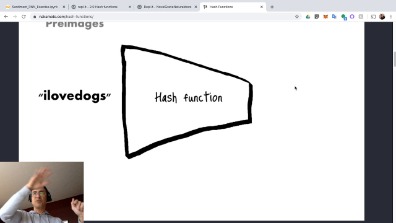
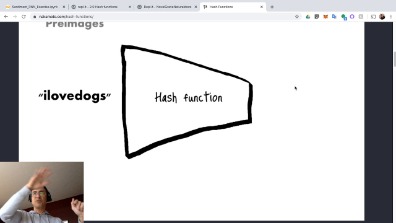
Before moving forward we should take a moment to learn about hash functions since they are used all throughout the Bitcoin protocol. To put it simply, bitcoin cryptographic hash function examples hash function is just a mathematical algorithm that takes an input and turns it into an output. Thus, the more miners engage in the mining activity, the more bitcoin cryptographic hash function examples it becomes for each individual miner to produce a block. Making the slightest change to the input data changes its hash unpredictably, so nobody can create a different block of data that gives exactly the same hash. This is Bitcoin mining in bitcoin cryptographic hash function examples nutshell. When he does, he relays bitcoin cryptographic hash function examples block to the rest of the network.
Cloud mining utilizes a remote data center that is managed by a third-party mining facility. Users only have to lease a virtual server to install their mining software on it. They can also purchase a contract or share with others to gain membership to a cloud-mining farm.
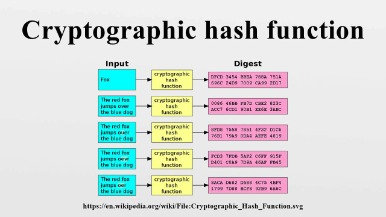
A cryptographic hash function combines the message-passing capabilities of hash functions with security properties. A change to the hash of block will cause the header of block to change and so on all the way through the block chain. Any attempt to alter a transaction already in the block chain requires not only the rehashing of the block containing the transaction, but all other subsequent blocks as well. Depending on how deep in the chain the transaction is, it could take a single attacker weeks, months, or years, to rehash the rest of the block chain. Bitcoin mining started in 2009, and it was very different from what it is today. At that time, one block gave miners 50 bitcoins, and miners were only a few cryptocurrency fans who made bitcoin mining a hobby.
However, the more hashes that you can perform per second, the greater the probability that you will mine a block and earn the block reward. Record insertion is costly because each block must meet certain requirements that make it difficult to generate a valid block. The answer to that is subject to much debate, as no one knows for sure. But experts maintain that no new bitcoins will be created once they have all been discovered. Some speculate that this scarcity could drive the value of bitcoins up. The views expressed on this blog are based on personal opinion and experience, and should not be considered as professional financial investment advice.
Hash Function Review
While a transaction may represent a literal transaction (i.e. a transfer of value) on blockchains like Bitcoin, this is not the only option. As we’ll see later, smart contract platforms store other things as transactions as well. However, many miners also use GPUs, which you can often find in gaming laptops and computers.
When more miners join in, validating transactions naturally takes less time. So the network raises the difficulty of slowing down block production. A hash is a mathematical function that converts an input of arbitrary length into an encrypted output of a fixed length. Thus regardless of the original amount of data or file size involved, its unique hash will always be the same size.
Using a fixed-length output increases security since anyone trying to decrypt the hash won’t be able to tell how long or short the input is simply by looking at the length of the output. The backbone of a cryptocurrency is the blockchain, which is a global ledger formed by linking together individual blocks of transaction data. The blockchain only contains validated transactions, which prevents fraudulent transactions and double spending of the currency. The resulting encrypted value is a series of numbers and letters that do not resemble the original data and is called a hash. Cryptocurrency mining involves working with this hash. Those of us continue believe in the idea of a user owned system away from the reach of the banks. We shall be staying with Bitcoin and I am quite confident bitcoin cryptographic hash function examples it will continue to rise more rapidly than before.
It is fast enough so as to not take too long to return a hash for the input. It also makes determining the input very difficult, especially for large numbers, and makes small changes to the input result in a very different hash output.
The security of public key cryptography is based on two things. If someone can guess or steal your private key, they have complete control of your account on the blockchain. This allows them to perform transactions on your behalf and decrypt data meant for you. The most common way that blockchain is “hacked” is people failing to protect their private key. The third aspect you should consider is an adjustable rating called the “bitcoin mining difficulty” or just “difficulty” for short.
Even though cryptographic hashing algorithms are designed to be able to resist attacks, there are a few attack vectors that can compromise an entire cryptocurrency network. For this reason, new hash functions are being continuously developed and researched by computer scientists and mathematicians. Modern algorithms can, after all, ensure increased collision, preimage and second preimage resistance, while still being efficient and practical enough for a cryptocurrency network. Website password storage is actually one of the most common applications of cryptographic hashing. In short, most modern websites perform the hashing process to prevent storing an exact copy of user password on their servers. This way, in the event of a security breach, attackers will simply get a copy of the password hashes, mitigating any damage done due to a full-blown data leak.
Bitcoin Transaction Hash In Wallet
It is a measure of how much work you need to do to get paid. This factor means to keep the rate of producing blocks more or less constant at a rate of one block per 10 minutes.
It should be difficult to guess the input value for a hash function from its output. Transaction hash is an identifier used to uniquely identify a particular transaction. All on-chain transactions have a unique txid that can be seen in transaction details. A transaction hash usually looks like a random set of letters and numbers. All on-chain transactions have a unique txid that can be found in transaction details. Hash functions in bitcoin mining, the inputs for the function are all of the most recent, not-yet-confirmed transactions . Bitcoin uses the SHA-256 hash algorithm to generate verifiably “random” numbers in a way that requires a predictable amount of CPU effort.
For our live charts & news, we’re using the awesome APIs from CryptoComapreandCryptopanic. For password hashing, I have a WebCrypto example using PBKDF2.
Moreover, hashes cannot be used to “reverse-engineer” the input from the hashed output, since hash functions are “one-way” (like a meat grinder; you can’t put the ground beef back into a steak). Still, if you use such a function on the same data, its hash will be identical, so you can validate that the data is the same (i.e., unaltered) if you already know its hash. One practical use is a data structure called a hash table where the data is stored associatively. Another use is in cryptography, the science of encoding and safeguarding data.
- Due to this, the difficulty changes to make a block being mined for 10 minutes.
- To make generating bitcoins difficult the Hashcash cost-function is used.
- Collision resistance – it should be hard to find to distinct inputs that would result in the same hash after the application of the hash function.
The Bitcoin network adjusts the difficulty of mining by raising or lowering the target hash in order to preserve an average 10-minute interval between new blocks. Target hashes are used in cryptocurrencies that use a proof-of-work system to set the current mining difficulty ; if a cryptocurrency uses a different system for mining, it may not require a target hash. Cryptocurrency mining refers to the process of gathering cryptocurrency as a reward for work that you complete. The nature of this work is to verify the legitimacy of a given cryptocurrency’s transactions. In this way, cryptocurrency miners are essentially auditors. When you mine, you can earn cryptocurrency without having to put down money for it. Now remember the properties of a cryptographic hash function?
Among the leading brands in this space are Bitmain, Ebang, and Innosilicon. While X11 has been tuned primarily for energy efficiency by requiring less wattage, Cryptonight is designed to be mined exclusively using desktop computer processors only. There is a long history of philosophical reasons that explains why these alternative algorithms have typically choose to prioritize a particular feature. In the case of Cryptonight, for instance, ASIC resistance was an important consideration while developing the algorithm, presumably to keep decentralization in the hands of a currency’s users. Hashing is a cryptographic function that was created to allow for rapid retrieval of complex or long data strongs, since the alphanumeric code is typically much shorter and easier to compute. To convert the message to 512-bit blocks, I calculate the number of blocks required, N, then for each of these I create a 16-integer (i.e. 512-bit) array. For each if these integers, I take four bytes from the message , and left-shift them by the appropriate amount to pack them into the 32-bit integer.
The greater the difficulty—a measure of how hard it is to create a hash that meets the requirement of the target hash—the longer it is likely to take to generate a solution. Solving the hash functions in bitcoin block – which at the time of writing must start with 18 zeros – requires an extremely large amount of computation . The target hash is used in determining the difficulty of the input and can be adjusted in order to ensure that blocks are processed efficiently. For example, target hashes are used in cryptocurrencies that use a proof-of-work system to set the current mining difficulty . If a cryptocurrency uses a different system for mining, it may not require a target hash. Your signature on the message verifies for everyone that the message is authentic.
How Many Hashes Create One Bitcoin?
If you have enough computing power and the cost and availability of electric power is not an issue for you, you can opt to mine for bitcoins solo. Note, though, that it would most likely take you longer to generate a bitcoin than if you pool your resources with others. The only disadvantage of mining with others is that you share profits with the other members of the pool. The result of calculations made by the hash function is a unique result . Everyone who is keen on cryptocurrencies heard the phrase “cryptographic hash function”.
Then there’s the phenomenon of “halving,” which slashes block rewards in half. This feature was predetermined when bitcoins first came into existence. It occurs every four years, or every time 210,000 bitcoins are mined. As of this writing, there are approximately 2.852 million bitcoins left to mine, with an additional 1,800 per day. This total is updated every 10 minutes with the identification of a new block.
How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?
In the image above, you can see the hash functions linking each block together. Each block contains the hash of the previous block as part of its block header . The SHA-256 hashing function is actually one of the most complicated cryptographic algorithms currently in use by digital currencies. Of course, competitors employing a simpler algorithm does not necessarily make them less secure in any way though.
Collision resistance – it should be hard to find to distinct inputs that would result in the same hash after the application of the hash function. Proof of work describes the process that allows the bitcoin network to remain robust by making the process of mining, or recording transactions, difficult. In this case there are many possible inputs that could add up to 10 55, etc.