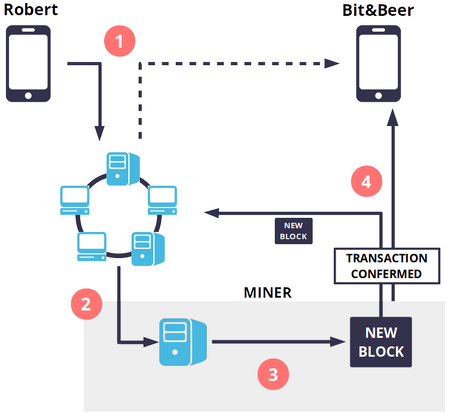
When a cryptocurrency transaction is made, that transaction is sent out to all users hosting a copy of the blockchain. Specific types of users called miners then try to solve a cryptographic puzzle (using software) which lets them add a “block” of transactions to the ledger. Whoever solves the puzzle first gets a few “newly mined” coins as a reward (they also get transaction fees paid by those who created the transactions). Sometimes miners pool computing power and share the new coins.
People who are running software and hardware aimed at confirming transactions to the digital ledger are cryptocurrency miners. Solving cryptographic puzzles (via software) to add transactions to the ledger (the blockchain) in the hope of getting coins as a reward is cryptocurrency mining. Over time, this means that bitcoin wallets end up with lots of addresses containing varying amounts of bitcoin and change from bitcoin transactions. When you send bitcoins to someone, your wallet will try its best to piece together the necessary funds using the addresses containing the different amounts.
The digital currency known as Bitcoin was created in 2009 by a person or organization using the alias Satoshi Nakamoto. The real identity of Satoshi Nakamoto has never been established. There are no physical bitcoins that correspond with dollar bills and euro notes.
Like all wallet providers, Blockchain.info has absolutely no control over this, and cannot expedite transactions. This is always dependent upon the bitcoin network of miners, which we are not a part of. The blockchain is like a decentralized bank ledger, in both cases the ledger is a record of transactions and balances.
Many reports suggest that many buyers lose their investments on exchanges and mining losses. Exchanges are more likely to hacked — even if you have the protection of a smart wallet. Additionally, if you do have a wallet and you forget or misplace your key, there is rarely a way to retrieve your coins.
Ledgers known as blockchains are used to keep track of the existence of bitcoin. It can be given directly to or received from anyone who has a bitcoin address via peer-to-peer transactions. Bitcoin also trades on various exchanges around the world, which is how its price is established.
Carefully research your cryptocurrency wallets to be sure you have the most reliable option. If it eventually is rejected, then the funds would remain at the bitcoin address they were sent from. The only thing you can do at this point is to wait and see if the transaction is accepted into a block.
How Can I Buy Bitcoin?
All transactions are broadcast to the network and usually begin to be confirmed within minutes, through a process called mining. The block chain is a shared public ledger on which the entire Bitcoin network relies. It allows Bitcoin wallets to calculate their spendable balance so that new transactions can be verified thereby ensuring they’re actually owned by the spender. The integrity and the chronological order of the block chain are enforced with cryptography.
How do you use Bitcoin transactions?
Bitcoin Confirmations. Roughly every ten minutes, a new block is created and added to the blockchain through the mining process. This block verifies and records any new transactions. The transactions are then said to have been confirmed by the Bitcoin network.
- The real identity of Satoshi Nakamoto has never been established.
- The digital currency known as Bitcoin was created in 2009 by a person or organization using the alias Satoshi Nakamoto.
For starters, bitcoin’s volatility is a big reason why most retailers won’t accept it. According to online blog Blockonomics, Dell, Expedia, Microsoft, PayPal, and Stripe have all dropped payment support for bitcoin.
If the majority of users trying to solve the puzzle all submit the same transaction data, then it confirms that the transactions are correct. Each block is connected to the data in the last block via one-way cryptographic codes called hashes which are designed to make tampering with the blockchain very difficult. Bitcoin mining is a critical cog in the cryptocurrency machine since it is the process which validates transactions and secures the Blockchain from unlawful interference. Mining gives legitimacy to Satoshi Nakamoto’s vision, enabling a decentralised and democratic system to manage Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
Transactions – private keys
A transaction is a transfer of value between Bitcoin wallets that gets included in the block chain. Bitcoin wallets keep a secret piece of data called a private key or seed, which is used to sign transactions, providing a mathematical proof that they have come from the owner of the wallet. The signature also prevents the transaction from being altered by anybody once it has been issued.
How Bitcoin Mining Works
How are transactions verified in Bitcoin?
A transaction is a transfer of value between Bitcoin wallets that gets included in the block chain. All transactions are broadcast to the network and usually begin to be confirmed within 10-20 minutes, through a process called mining.
On one hand, there’s the digital token, which is what cryptocurrency investors are buying. And on the other hand, there’s the underlying blockchain, which is that aforementioned digital ledger that transparently and immutably records transactions. Blockchain is where the real evolution and innovation of the cryptocurrency movement lies. At today’s price, that works out to close to $135,000 per bitcoin block reward. But with this reward being halved in May 2020 to 6.25 bitcoin per block solved, investors and miners have historically bid up the digital token about a year in advance of a halving event.
Blockchain describes the way transactions are recorded into “blocks” and time stamped. It’s a fairly complex, technical process, but the result is a digital ledger of cryptocurrency transactions that’s hard for hackers to tamper with.
Cryptocurrency is technology-based, which leaves this investment open to cyberattacks. Hacking is a serious risk, since there is no way to retrieve your lost or stolen bitcoins.
Bitcoin 101
It should be said that while many of these companies cited volatility as a reason to drop bitcoin, variable transaction fees were noted, too. Cryptocurrencies are usually built using blockchain technology.